[참고] Chapter 2. The Structure of the Java Virtual Machine
Chapter 2. The Structure of the Java Virtual Machine
Conditional branch: ifeq, ifne, iflt, ifle, ifgt, ifge, ifnull, ifnonnull, if_icmpeq, if_icmpne, if_icmplt, if_icmple, if_icmpgt if_icmpge, if_acmpeq, if_acmpne.
docs.oracle.com
1. Java Compile & Run
1-1. Java Compile & Run 과정
- .java 파일 생성
- Java Compiler (javac)로 .java 파일 컴파일 .java → .class
- JVM에서 메인 .class 파일 실행
- Class Loader : .class 파일을 JVM에 로드
- Byte Code verification
- Just-In-Time Compiler로 execute
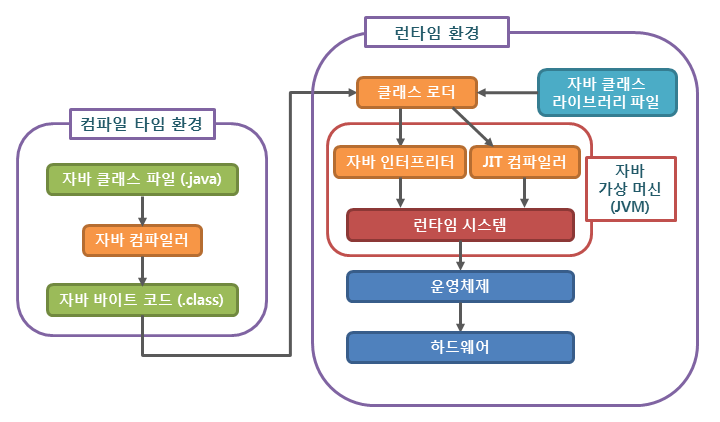
1-2. Java Byte Code
- JVM이 이해할 수 있도록 컴파일된 바이트 코드 (binary format)
- Byte : 코드 명령어 크기가 1 byte
- 확장자 : .class
- JVM만 있으면 어느 운영체제에서도 실행 가능 (machine-independent encoding)
1-3. JVM
- 운영체제에 종속적 (machine-dependent)
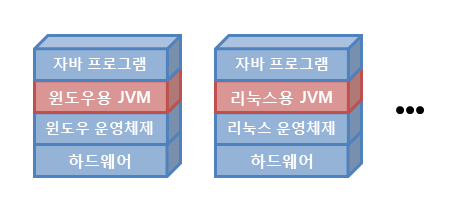
- 구성 요소
| Class Loader | 동적으로 클래스를 로드 |
| Interperter | 바이트 코드를 읽고 해석 |
| Just-In-Time compiler | 실제 런타임에 바이트 코드를 기계어로 변환 |
| Garbage collector | 더 이상 사용하지 않는 메모리 자동 회수 |
- Compiler vs. Decompiler
| Compiler | Decompiler |
| .java → .class | .class → .java |
| Java Soucre Code → Byte Code | Byte Code → Java Source Code |
2. The Structure of the JVM
2-1. The class File Format
- JVM으로 실행되기 전 컴파일된 Java Code
- HW & OS Independent binary format
2-2. Data Types
- JVM Type Checking
- 이미 런타임 이전에 컴파일러 의해 완료됨을 가정함 (JVM 자체에서 진행 X)
- JVM Operating Type
| 1) primitive | 실제 데이터 저장하는 값 | boolean, byte, char, short, int, long, float, double |
| 2) reference | 데이터 객체를 참조하는 주소값 메모리 번지수 (pointer 개념) |
Integer, Long, Double, Float, Boolean, Byte, Short, Char |
- Primitive Types
| numeric | integral | byte (8-bit) | -128 to 127 (-2^7 to 2^7 - 1) |
| short (16-bit) | -32768 to 32767 (-2^15 to 2^15 - 1) | ||
| int (32-bit) | -2147483648 to 2147483647 (-2^31 to 2^31 - 1) | ||
| long (64-bit) | (-2^63 to 2^63 - 1) | ||
| char (16-bit) | 0 to 65535 | ||
| floating-point | float | * Nan : Not-a-Number value (ex. dividing zero by zero) |
|
| double | |||
| bool | boolean | JVM int data type으로 컴파일됨 | |
| returnAddress | pointers | pointers to the opcodes of JVM instructions |
- Reference Types
- array types
- class types
- interface types
2-3. Run-Time Data Areas
JVM은 다양한 run-time data areas 제공 (JVM or Thread의 시작과 종료를 따름)
2-3-1. PC Register
- JVM은 한번에 여러 개의 Thread 처리 가능, 각 Thread는 각자의 pc register 가짐
- JVM Thread는 매 순간 single method 코드 실행함
- native single method : PC Register는 최근 수행 JVM instruction 주소를 포함
- not native single method : PC Register value = undefined
- PC Register는 충분히 커서 returnAddress, native pointer도 저장 가능
2-3-2. Stacks
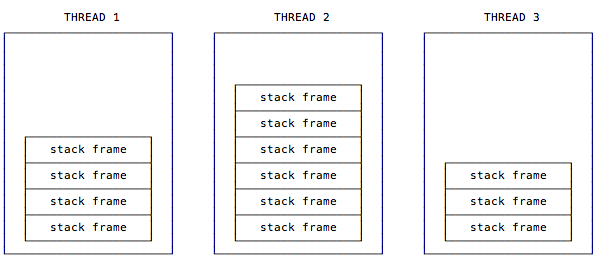
- 모든 JVM Thread는 각자의 Stack 가짐
- Stack은 각 Thread 생성 시점에 같이 생성됨
- Stack은 frame을 저장 (local variables, partial results)
- Size
- fixed : Stack 생성 순간에 size 결정됨
- dynamically expand : 연산에 의해 필요한 만큼 달라짐
- 관련 에러
- StackOverFlowError : fixed size stack인데 연산에서 더 큰 size 필요
- OutOfMemoryError : dynamically expand stack인데 메모리 부족
2-3-3. Heap
- 모든 JVM Thread들이 공유
- JVM start-up 할 때 생성
- 전체 class instances, arrays가 할당되는 메모리
- Garbage Collection 이루어짐
- 사용 끝낸 Heap의 Storage 반환
- object의 storage가 반환됨 (O), object가 반환 (X)
2-3-4. Method Area
- 모든 JVM Thread들이 공유
- JVM start-up 할 때 생성
- per-class structure 저장
- run-time constant pool (static field)
- field, method area
- code for method/constructors
2-3-5. Run-Time Constant Pool
- 다양한 종류의 constant 포함
- numeric literals
- field references
- JVM Method Area 의해 할당됨
2-3-6. Native Method Stacks
- Java 외 다른 언어로 작성된 Native Method 지원하기 위한 stack
- size : fixed / dynamically expand
2-4. Frames
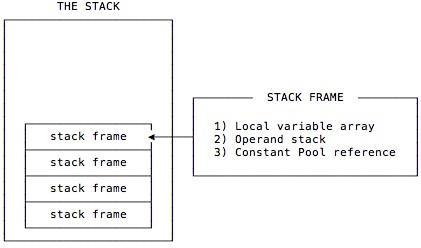
- Thread에 의해 생성된 frame은 local (다른 Thread에 의해 참조될 수 없음)
- JVM Stack에 할당됨
- 역할
- data, partial results 저장
- dynamic linking 수행
- method 위한 value return
- exception 발생
- 생명주기
- method 호출될 때마다 새로운 frame 생성
- method 호출 완료 시, 파괴됨 (method 정상 수행 여부는 고려 X)
- 각 frame마다 고유의 자원 가짐
- array of local variable
- operand stack
- reference to rune-time constant pool of the class of the current method
- Current Frame
- Thread에서는 오직 하나의 Frame만 executing method 위해 활성화
- local variables, operand stack의 operations는 보통 current frame 주소 가지고 있음
- 현재 current frame의 method 완료되거나 다른 method 호출 시작하면 기존 current frame은 자리에서 물러나고, 새로운 frame이 생성되면서 current frame으로 등극
- 새로운 current frame return하면 그 결과를 이전 frame에게 전달
3. JVMTI
- 정의
- Java Virtual Machine Tool Interface
- Programming interface used by development and monitoring tools
- 역할
- VM state에 접근하기 위한 VM interface 제공 (profiling, debugging, monitoring, analysis ...)
- profiler는 JVMTI를 매개로 JVM과 소통
- 특징
- 2-way interface (JVM ↔ Agent)
- Byte Code Instrumentation 이용
- profiler가 profiling info 수집하기 위해서는 해당 profiled application의 byte code를 수정해야 함
- 프로파일에 유의미한 부분에 supporting byte code instructions 삽입
- Target Application의 일반 실행을 방해하지 않고 독립적인 process 제어 가능
4. Agent

- 정의
- JVM에서 동작하는 Java Application 중 하나
- JVM에서 running application의 상태 관찰 & 실행 제어
- 특징
- Event를 통해 발생 사건 인지
- JVMTI를 매개로 Agent ↔ JVM 소통
https://dramatic-lift-c67.notion.site/Java-7-JVM-1a2fdfc4a3d64ca5814f4504ccf416f1?pvs=4
Java 7 기준 JVM 정리 | Built with Notion
📅 Schedule
dramatic-lift-c67.notion.site
Java 17 기준 JVM Tool Interface | Built with Notion
🔍 질문
dramatic-lift-c67.notion.site
'인턴일지 > 슈어소프트테크' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [인턴일지 #6] Java GC, Heap Dump (0) | 2023.10.28 |
|---|---|
| [인턴일지 #5] Java Profiling, Profilers (0) | 2023.10.28 |
| [인턴일지 #3] 자사 도구 분석 (0) | 2023.09.19 |
| [인턴일지 #2] 프로젝트 정리 (0) | 2023.09.19 |
| [인턴일지 #1] 첫 출근 (0) | 2023.09.19 |



